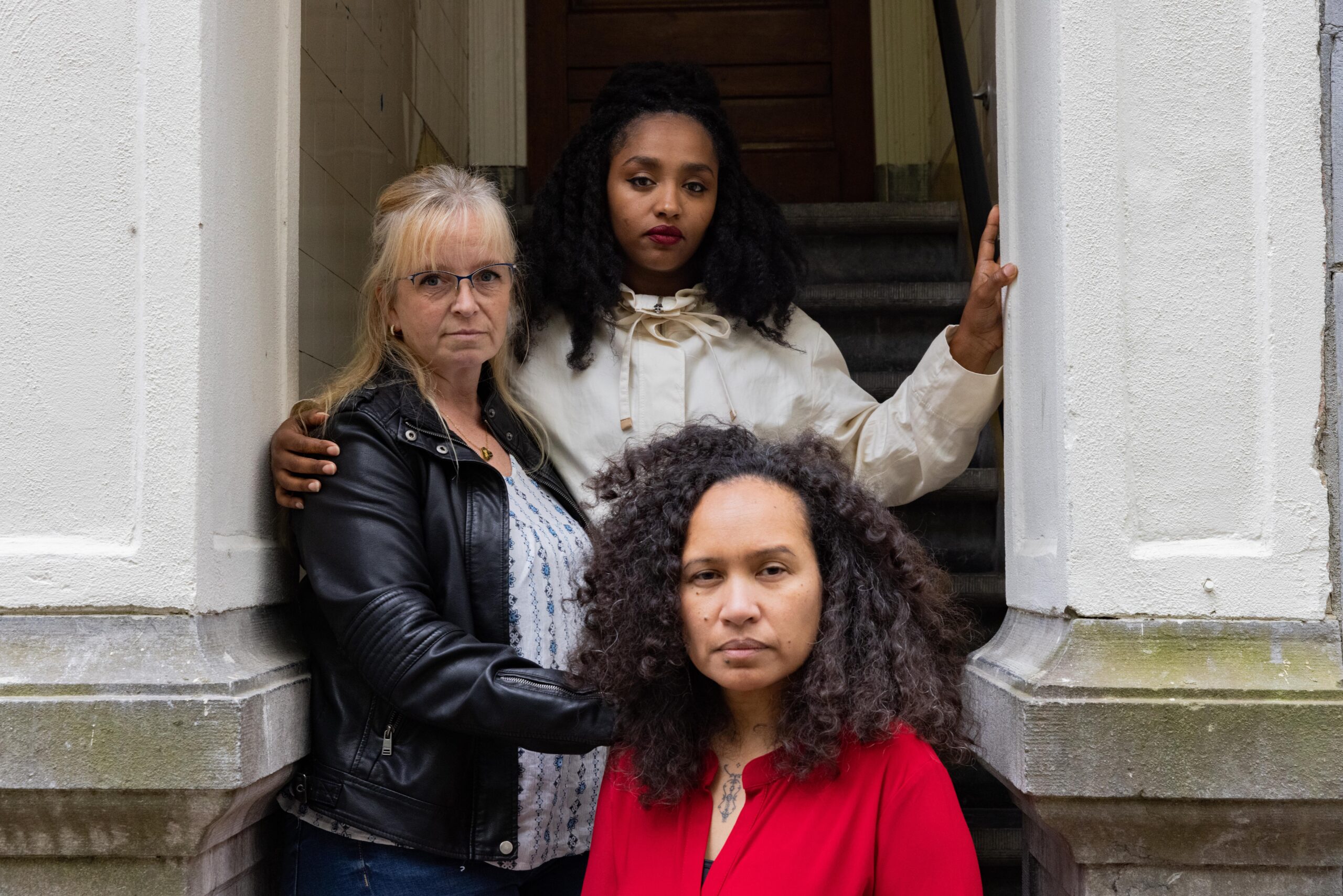
The government has recognized its error and resigned, but the women’s lives are still in tatters.
Franciska Manuputty’s ordeal with the Dutch tax authorities began in 2010, when she received notification to repay €30,000 (about US $35,000) in childcare tax benefits, to which the government alleged she had not been entitled. Manuputty, 49, is a low-income single mother of two. She was soon behind on the rent, couldn’t pay her electricity bills, and turned to a food bank to feed her family. Her daughter, now 20 years old, told her recently that as a child she had lived in constant fear of returning home from school to discover they had been evicted from their apartment.
Manuputty is one of the victims of what the Dutch media calls the child benefits scandal. Over the course of around a decade the government falsely accused thousands of eligible families of having committed fraud and ordered them to repay childcare tax benefits to which they had, in fact, been entitled.
A parliamentary investigation published in December 2020 found that the tax authorities had set up a child benefits system with bureaucratic rules so rigid that even the smallest administrative error in filling out forms caused the system to flag beneficiaries, who were then pursued by the courts and forced to repay all the money they had received—plus fines. The total number of victims is not yet clear; but based on a parliamentary investigation and the number of people who applied for the initial compensation of €30,000 (about $35,000), at least 35,000 people have been affected.
The fallout from the scandal led to the government’s resignation in January 2021.
Families that were forced to repay tens of thousands of euros faced bankruptcies, job losses, forced sale of houses, homelessness, divorce—even suicide. Several families saw their children removed by child protection authorities, on the basis that they were no longer able to care for them after losing their homes and financial stability.
The €30,000 compensation doesn’t even begin to solve Manuputty’s problems. Because the tax authorities labelled her a cheat in 2009, her name is now in the system and her credit is ruined. Over the past decade all her applications for financial aid were rejected, which forced her to keep borrowing money and leave bills unpaid. She now owes €100,000 ($115,000) to various creditors. “I hold on to life for my children,” said Manuputty.
Investigative journalists discovered, via the parliamentary freedom of information act, that the algorithms had been designed to flag “cheats” based on the amount a parent received—i.e., the more benefits they received, the more likely they were to fall under suspicion. The result: the people targeted were those whose low-paid jobs made them most eligible for childcare benefits.
A disproportionate number of people in that group were single mothers with foreign citizenship, so the algorithm de facto flagged poor women who were either immigrants themselves or the children of immigrants, adding racism to the scandal. The Ministry of Finance brought a discrimination suit against the tax authorities, but the public prosecutor dismissed the case, saying the issue must be solved politically. Victims of the false accusations are appealing that decision. A parliamentary commission will be appointed to investigate the matter later this year or next year.
Via a WhatsApp group for victims of the scandal, Franciska Manuputty met Batya Brown, 35, a part-time employee at a daycare center who is now pregnant with her fifth child. When the two were asked to address an anti-racism demonstration about their experiences they decided to collaborate on their speeches and provide one another with moral support. They were joined by Kristie Rongen, 45, a small truck driver, who had recently confronted Prime Minister Rutte during a widely viewed live broadcast of a political TV show.
While Rongen holds only Dutch citizenship, Batya Brown was born in Ethiopia. Manuputty’s parents are from the Maluku Islands, formerly a Dutch colony—now occupied by Indonesia. For the latter two women, their relationship with the Dutch state is informed by their ethnic identities, which is further compounded by the role that racism played in the tax scandal.
Brown was adopted as a child from Ethiopia, arriving in the Netherlands when she was six years old. Because of a bureaucratic error that she is fighting to correct, she is still ineligible for a Dutch passport. Meanwhile, in 2007 the tax authorities began demanding that she repay her benefits . The resulting financial problems forced her to move often and, while the tax authorities recently annulled her remaining debts, her struggle with the immigration authorities continues. In other words, she has been battling with both the tax authorities and the immigration office for her entire adult life.
Manuputty suffers from post-traumatic stress disorder and transgenerational trauma. Her grandfather is a South Mollucan, a member of an Indonesian indigenous group that fought in the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army (KNIL) alongside colonial forces in the Indonesian War of Independence (1945-9), then were brought to the Netherlands after the Dutch reneged on a promise to grant them territorial sovereignty. The Mollucan community feels humiliated to this day by their treatment at the hands of the Dutch. “As a victim of the child benefit scandal, I have been neglected and robbed of my dignity again,” said Manuputty, adding that she felt as though history were repeating itself.
Rongen acknowledged that she presents in her media appearances as a strong woman, which she is; but behind the scenes she is emotionally devastated. “I cry a lot, every day,” she said. Her ordeal with the tax authorities began in 2010, with her debt topping out at €92,000 ($123,000). After four years of debt counselling, the government annulled what was left of that amount and granted her compensation in December 2020. Her battle with psychological trauma is ongoing. She has dedicated herself to helping reunite parents with children they lost to foster care, a calling that provides her with a feeling of purpose. “When a mother messages me for help, I dry my eyes and get going again,” she said. In a matter-of-fact tone she added, “I would prefer not to live anymore. But what would happen to my children if I were no longer here?”
In addition to their media appearances and participation in anti-racism demonstrations earlier this year, the three women have initiated demonstrations of their own, to garner public support and amplify their demands. These include: cancellation of all the victims’ debts by the end of 2021; financial compensation of at least €1 million ($1.16 million) to each victim; and the immediate reunification of parents with children who were taken from them and put into foster care. They also want psychological support. And they want those responsible for the scandal to be brought to justice.
When the government resigned in January the women hoped the new administration would deal with the matter quickly, but they now understand the process will take years. One egregious reason for the slow pace: the commission tasked with defining the amount of compensation that each victim should receive is severely understaffed; at the current rate they will need 975 years to complete their work.
“Applying for everything costs so much time and energy, which I would prefer to dedicate to my children,” said Batya Brown. Kristie Rongen added: “Instead of asking for more effort from the victims, they should just give every one of them half a million euros to settle the matter. Our lives have been destroyed.”
Franciska Manuputty agrees. “I have been trying for years to regain my independence by setting up my own business,” she said, explaining that her applications for business loans have all been rejected because the “fraudster” label destroyed her credit rating. “I struggle for freedom, it’s in my genes, but I feel trapped in a prison without walls.”
The women have also reached out to other victims, organizing small events like picnics and activities for children, which they pay for via crowdfunding, just to relax and start healing together. Coming together has energized the women. “Our suffering has become visible,” said one. Then, with tears in her eyes and a voice choked with anger: “Years ago, when he was ten, eleven years old, I promised my oldest son that everything would be okay. He is 16 years old now! I am determined to keep my promise to him.”