Civil society organizations in Myanmar are pushing for international recognition of internet access as a human right.
Since the internet first emerged during the 2011 Arab Spring as an effective means of organizing grassroots protests and speaking directly to the rest of the world in an unprecedented way, human rights defenders have found that it can also be used as a weapon against them. Since 2011, nationalist politicians in both authoritarian and democratic states have learned how to manipulate their citizens through social media—and when to use internet shutdowns to cut their critics off from the rest of the world. The Myanmar military clearly understands this dichotomy well. Since seizing power on January 31, it has restricted internet access—starting with Facebook, which for most people in Myanmar is their primary gateway to the online world.
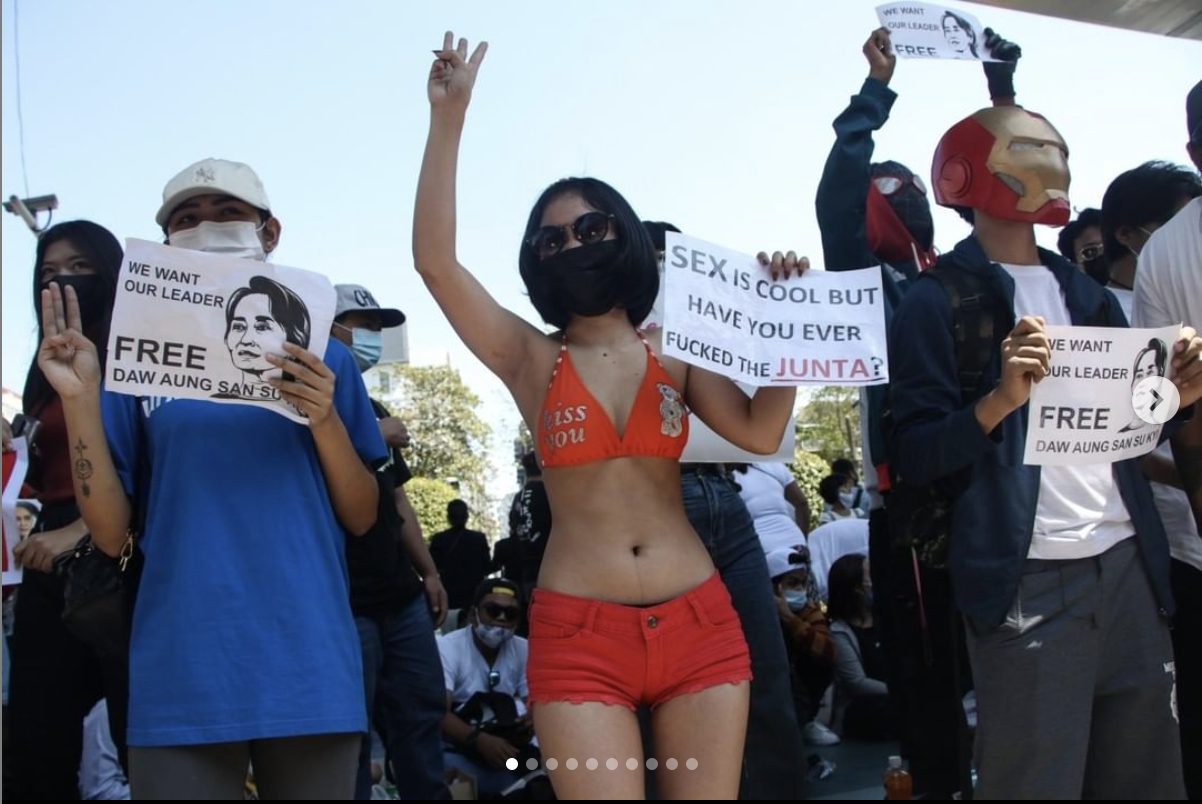
In the midst of massive peaceful protests and a violent response from the military, people inside Myanmar have attempted to get information out during first a partial and then nearly total internet shutdown. It has never been easy for human rights defenders in Myanmar, but without the internet it is exponentially harder.
This is not the first time the Myanmar government has limited or blocked internet access. Eight townships in Rakhine and Chin states have been living with shutdowns off and on since June 2019. The military reportedly lifted those shutdowns on February 3, even as they began to restrict access elsewhere. Without access to the internet during the pandemic, residents— many of them survivors of the military’s genocide against ethnic Rohingya—have been denied essential information and vital aid. Now there are signs that internet shutdowns will be the new normal in Myanmar.
#WhatIsHappeningInMyanmar?
Using this hashtag and others, people inside Myanmar have been doing their best to report events on the ground, although Facebook, WhatsApp, and Messenger have been blocked since February 3. Many people, including activists and journalists, moved to Twitter, where they called for the world to pay attention and support them. The military responded by blocking access to Twitter and Instagram on February 5, and followed this with a broader internet shutdown. For a few days, friends and family outside of Myanmar had no information; they were left to wonder whether their loved ones were safe. Only a few independent media outlets and individual activists, such as journalist Mratt Kyaw Thu, managed to circumvent the shutdown and post live updates to social media.
Internet access now appears to be at least partially restored. Footage of protests, including a video of the military shooting 19-year old Myat Thet Thet Khaing, is making the rounds on social media; but military leaders refuse to back away from their anti-democratic coup, despite international condemnation and the imposition of sanctions by the United States.
In fact, the military has proposed a draconian “cyber security bill.” According to an open letter signed and posted online by 161 Myanmar civil society organizations—a brave move, given the ongoing arrests of members of the National League for Democracy party as well as Union Election Commission officials and high-profile activists— the bill:
…includes clauses which violate human rights including the rights to freedom of expression, data protection and privacy, and other democratic principles and human rights in the online space. As the “bill” is drafted by the current military regime to oppress those who are against its rule, and to restrict the mobilization and momentum of online resistance, we strongly condemn this action by the current military regime in accordance with our democratic principles.
Currently there are only unofficial English translations of the bill available on social media, but reviews by Reuters and BBC reporter Freya Cole confirm that the legislation would prohibit “speech, texts, image, video, audio file, sign, or other expressions disrupting unity, stabilization, and peace.” The text also appears to include provisions that would enshrine the government’s right to shut down the internet at will and require Internet Service Providers to retain massive amounts of user data. ISPs that do not comply could be subject to fines and see their employees imprisoned.
The internet as a weapon
The military knows from its own experience the power of the internet—and especially of social media. The consensus among international experts and the U.N. is that the genocide of the Rohingya was enabled by the military’s use of Facebook; this is something that even Facebook acknowledges.
In a 2018 article on the role Facebook played in inciting against the Rohingya, The New York Times reported that the military created fake Facebook personas who “posed as fans of pop stars and national heroes” and “flooded” the social media platform with hatred, spreading misinformation and fear about Muslims generally and the Rohingya specifically, even as the military systematically massacred and raped Rohingya, burning their villages to the ground and forcing the survivors to flee to neighboring Bangladesh.
Facebook provided some shocking statistics about posts in Myanmar during the genocide of the Rohingya. In a 2018 blog post the company says it removed “425 Facebook Pages, 17 Facebook Groups, 135 Facebook accounts and 15 Instagram accounts in Myanmar” for engaging in “Coordinated Inauthentic Behavior” (CIB)—i.e., networks of fake accounts dedicated to inciting violence and hatred and spreading misinformation. According to the company “[a]pproximately 2.5 million people followed at least one of these Facebook Pages.”
But that wasn’t the end of the matter. Facebook has continually reported on efforts remove CIB— yet some of this content is still active. In fact, the social media platform banned a military television network page that was operating after the coup had already taken place only because the Wall Street Journal asked why it was still active, given that it had been banned earlier.
#SaveMyanmar
We do not have any clarity on what will happen next to internet freedom in Myanmar. For social media users outside the country, this a good time to follow the Twitter accounts of people who have been reporting events from the ground as much as and whenever possible. Twitter should consider authenticating these accounts and fast-tracking a blue check of verification to those who request it.
In a February 6 letter, civil society organizations in Myanmar called for Internet Service Providers to “prevent the military from accessing user data…take every action available to appeal the recent junta directives, [and] develop plans in the event the human rights situation in Myanmar deteriorates.” The situation in Myanmar is inarguably deteriorating, and ISPs must develop those plans now. Telenor, the Norwegian multinational communications services provider, has said repeatedly that it is doing everything it can to push back on these orders, but their best is clearly not enough.
The UN Human Rights Council is holding an emergency session on Friday to discuss the “implications” of the situation in Myanmar. The UN has already taken steps towards declaring access to the internet a human right. As it considers how to support human rights in the country it should emphasize the need to maintain internet access.
After all, the internet isn’t just a weapon; it is still, even now, and despite those who continue to abuse it for nefarious purposes, a tool for upholding human rights and maintaining democracy.